Learn more:
"Viz Artist Introduction to Scripting" free cource on Viz University
Why do we need scripts in VizArtist?
All the more so we have got a lot of ready plugins...
I like scripting because it enables to get non-existed functionality or remake existing with new options. You can significantly speed up your work, including creating complex structures, keyframes, etc. You can automize processes of getting and processing of data within a scene. Also, you can import coordinates of camera and objects from AE. The right way to create interactive elements is to use a script.
The script is a typical program. The only difference is in the level of abstraction. In classical languages, we operate with primitive data type like link, number, character. In scripts it's more convenient — high-level objects are already existing for use. For example, in vizrt-scripts, we work with containers and plugins, scenes and the engine. It's enough to assign a new position for the camera to make it to go over with natural consequences like view change.
The script is like a program. It works as an automate taking input data and giving result during a process. Input data can be anything like current container, position, mouse click or button-pushing... A result is also anything like changing of a parameter, creating or deleting anything. Of course, a script can return nothing. But why would we write it?
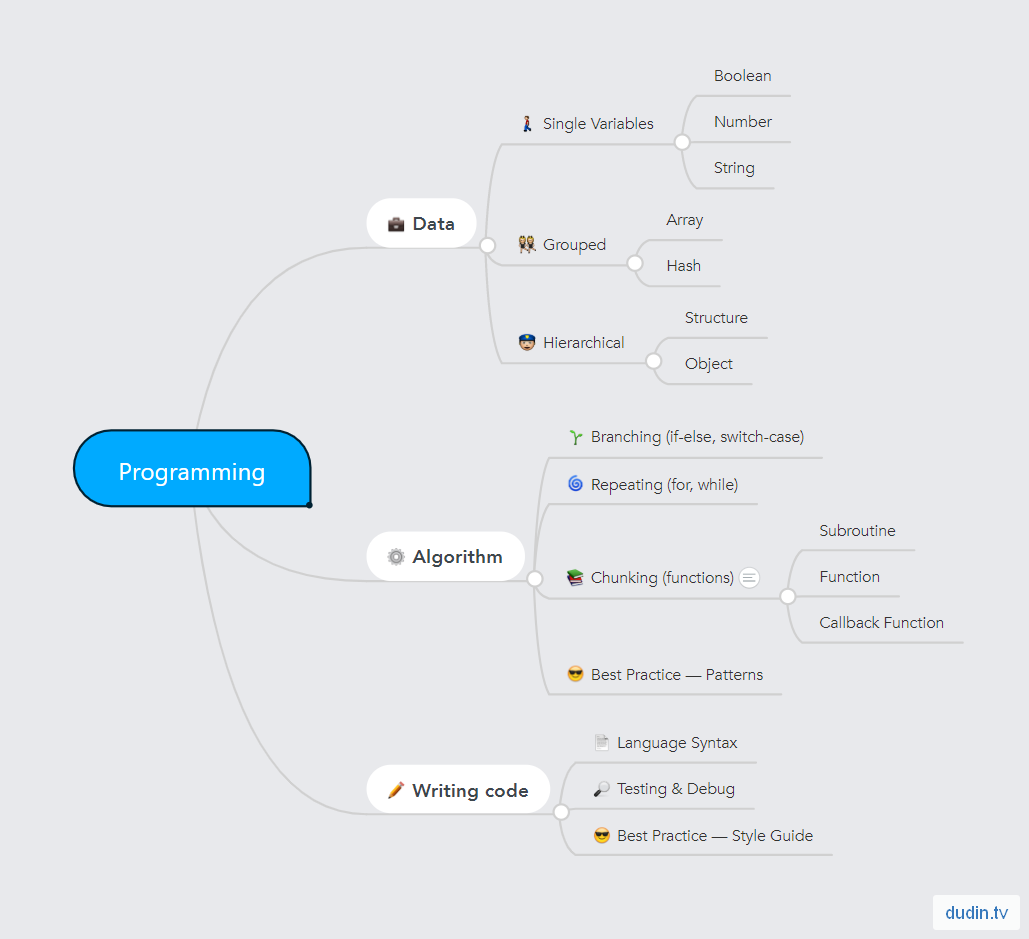
Learning any programming language contains three components:
- Form of data storage — variables, arrays, objects
- Logical constructions — branches, loops, functions
- Syntax — rules of code writing to make compiler understands it Wikipedia. In VizArtist we use language which is called "Viz 3 Script".
Data storage form and logical constructions are common for most programming languages. They have difference only in syntax. It's easy to learn during working because any mistakes are marked automatically by the compiler.
If you are a newbie in programming I strongly recommend you to watch a free online course "CS 50" from Harvard. The main idea you should endure is that the computer does exactly what you tell to do. Without auto thinking out, without auto assumptions, without auto finishing! You are fully responsible for what script does. In the best case, the computer will only prompt the line where is most likely an error.
Good news! There are only 7 concepts that need to be remembered and understood for the beginning. All the rest is a combination of them and syntactic features.
- Variable
- Branches (if else)
- Array
- Loop
- Function
- Object
- Callback function
1. Variable
The basic entity of programming. Variable is a link to a certain area of data. You can get by the name of a variable: a simple number, a text string, an array value or object (about arrays and objects a bit later)...
Side of the variable location around "=" is important. Example: x = y + z. If it located on the right from "=" (y and z), it converted into the values. If it located on the left from "=" (x), it used for storing new value.
A typical expression contains a left side variable, "=" sign and right side of an expression. The compiler first calculates value in the right side, then put the value to the left side variable. This is the reason why the left part can contain only one variable — it must be a place for data storing. But in the right part of expression can contain any expression.
angle = 360
new_angle = angle + 10
The variable new_angle will have got 370. angle + 10 -> 360 + 10 -> 370
We can conditionally divide the variables into pre-existing and custom:
- If you need pre-existing system variable — go to the documentation and find out how to name it. Just call it by name in the script.
- You can create your own variables. Then you can use them wherever you want. But it can be used within the script where it was declared.
Dim s As String — this is creating (declaring) of the string variable.
Vizrt-script is typed programming language. It's mean that all variables must be links to a particular type of data. No possible to declare a variable without type Dim varDim var As Variant. But the best way is to specify a particular data type! Thus you forbid to compiler put text to a number variable. But if you want to convert type you can do it anytime by system functions like var = CInt("42") (we got number 42 from string "42").
Variable types
Basic variable:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Integer | Dim i As Integer integer number (no floating point), represents integer from −2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647. Suit for counters and something which can be only integer. 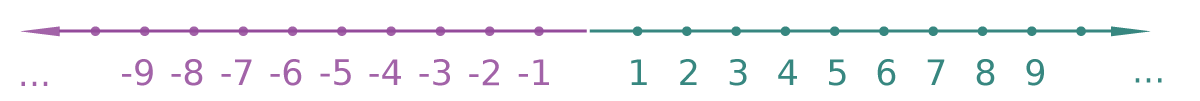 |
| Double | Dim f As Double Rational floating point number declaring in memory as an integer (fraction) multiplied by 10 in some degree (exponent). Thus, float number can cover a huge range of numbers from 10−308 to 10308. For example, f = 3,1415926535 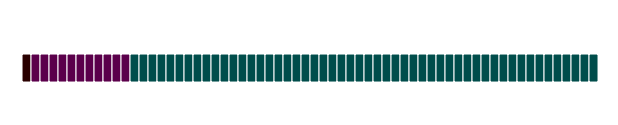 Float variable takes 64 bits. Float variable takes 64 bits. |
| String | Dim s As String Text. Any chars, line breaks, etc in any encoding s = "String\nText" |
| Boolean | Dim enable As Boolean Boolean variable represent only "true" or "false" enable = true. |
Complex variables:
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Vertex | Dim pos As Vertex Triple set of double-values. Perfect suit for store coordinates in 3D space: position, rotation, scaling. Vertex have access to separate axes x, y, z: pos.x, pos.y, pos.z. |
| Array | Dim arr As ArrayDouble Collection(list) of data in some single type. Adding new element: arr.Push(3,14159). Getting first element: arr[0] |
| Stringmap | Dim map As Stringmap Named universe collection of Variant data type. You can store there any data type. Access to each element is by string. For example map["age"] = 100 (integer) or map["name"] = "Dmitry" (string). If the element not exists it will be created. |
| Datetime | Dim dt As Datetime It's for storing date and time. You can use only date or only time. dt = GetCurrentTime(). |
| Matrix | Dim m As Matrix Matrix 4*4 of double-values. |
| Variant | Dim m As Variant A universal variable for storing anything. You can put in any data type. |
Vizrt variable:
Container (link on some container in scene tree), Director (animation director in the stage), Keyframe (a key of animation), Color, Material, Camera, Grid, Light, Texture, Channel, PluginInstance, FunctionPluginInstance, Clipchannel.
- The best practice is placing defining of all variables in the beginning of the script. Some variables are sometimes used like parameters with some default values.
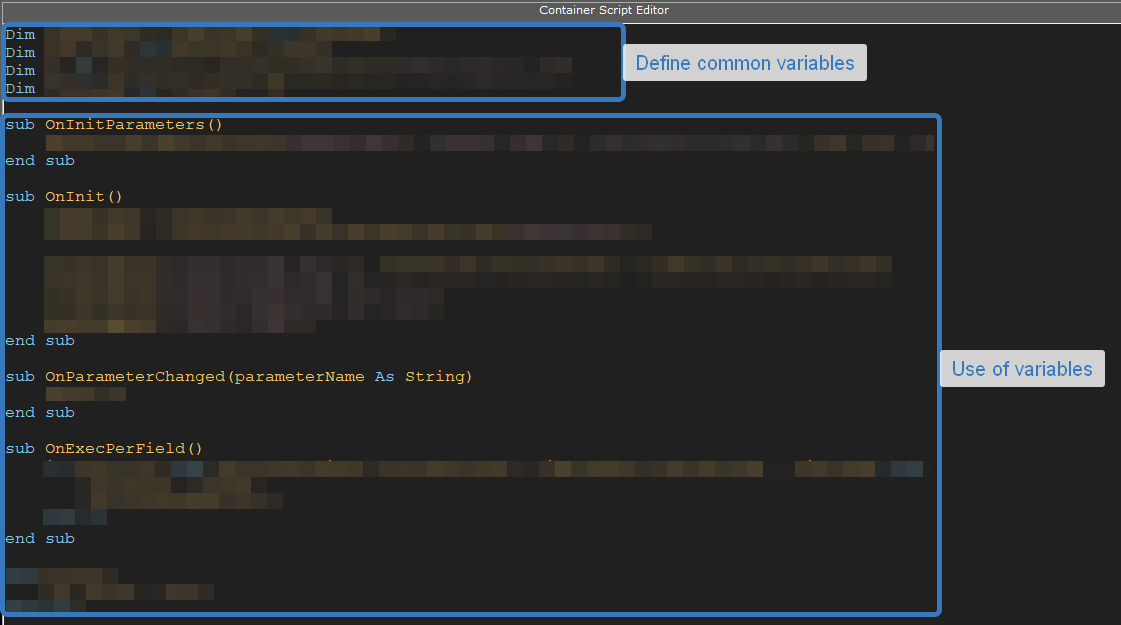
Conversion between data types
You can always change the data type by system functions as needed: CInt(var), CDbl(var), CStr(var), CBool(var). And there is a special function to turning from Double to String DoubleToString(value, precision).
2. Branching
Key benefits of any scripts are the branching — this is the ability to choose what to do along with a condition. In vizrt-script this realized by a construction If [condition] Then [do #1] Else [do #2] End If. Where instead condition must be a conditional value (boolean type). If you need only do #1—block than "Else do #2" you can drop out (don't write it).
Simple example from practice:
Dim temperature As Double = 17
Dim output As String
If temperature > 0 Then
output = "+" & CStr(temperature)
Else
output = CStr(temperature)
End If
With the standard conversion of the number into a string, the symbol "+" will not be added as expected. How to reveal the number with a "+" sign if the temperature above zero? "If else" help us. If a temperature greater than zero we get merging "+" with a number. If not then it's nothing to add.
Question for self-test. Which do we get "output" if the temperature will be equal 0?
Show the answer
Variable "output" is equal to the string "0". Because 0 is not greater than 0. Thus, we passed by the "true" branch and run only "false" part where we add nothing. 0 is not a negative number, so there isn't a minus sign. Good.3. Array
Frequently needed to store a list of some data. For example, a set of chart values. Creating unique variables for each value is cumbersome and extremely inconvenient for further processing.
Dim value1 As Double
Dim value2 As Double
Dim value3 As Double
or like this, more compact, but it's bad yet:
Dim value1, value2, value3 As Double
The simplest and convinient way is declare a variable as array data.
Dim values As Array[Double]
- To get or write the value in a specific cell of the array, you need to refer to its index
values[3]. - Index isn't a serial number! The index determines the offset from the beginning of the array! For getting the first value you need to refer zero index
values[0]. Because[0]is a zero shifting from the beginning.
Question for self-test. What is the minimum number of elements the array should contain so that the script does not generate an error with values[3]?
Show answer
values[3] — this is fourth element of array. That means array must contain 4 elements at least.
Sweety bonus. You can get element not only from the beginning of the array but from the end! To take the last element of the array, specify "-1" values[-1]. It's much easier and human-readable than values[values.ubound].
To get experience all the benefits of arrays, let's explore the loops.
4. Loop
Loop is a repeated part of code while the condition is true. There are three syntax styles of a loop in vizrt-scripts. Now we take only the most practical variant For [start] to [end] [do something many times] Next.
In start sets some default value for variable-counter. It increments by 1 with each repetition until value reaches to end value.
For i=0 to 10
array[i] = i
Next
Another kind of loop is "do while loop" syntax.
Dim i As Integer = 1
Do While i < 100
i = i * i + 1
println("i = " & i)
Loop
For Next is more convenient for arrays. Do While Loop more useful when you don't know how long it will work.
Note, any loop may be infinite! It's a very bad thing within vizrt-script. Infinity loop blocks the whole system! If VizEngine (VizArtist) catch this, it just emergency shutdowns the script until you restart it by hand or scene will be reloaded. So, please analyze a condition carefully. Have the condition any end value?
Most popular using of the loop is an array traversal. For example, let's calculate the arithmetic average in an array of numbers:
Dim sum, medium As Double
Dim values As Array[Double]
sum = 0
For i=0 to values.size-1
sum = sum + values[i]
Next
medium = sum/values.size
Exercise: write the script to find the minimum and the maximum values among array values.
Show answer
Dim values As Array[Double]
' fill up the "values"...
Dim min, max As Double
min = values[0]
max = values[0]
For i=1 to values.ubound
If values[i] < min Then min = values[i]
If values[i] > max Then max = values[i]
Next
Note:
- I used one-line "If" syntax. In this case "End If" is not obliged.
- loop starts from second element of array
For i=1, because we already considered the first element before the loop.
5. Function and subroutine
Function or subroutine is a named set of commands you can call from any place of the script. It's convinient for two cases:
- When you need to cut off a duplicating piece of code.
- For comfort, when you want to make script more human readable and structured code.
- To split code into separated actions which you can run independently.
Function or subroutines are similar to variables. By name of variable we get access to the data, we can read or rewrite. By name of function we call the code.
There is only difference in constructs function and sub, function always must return some value. But subroutine never return anything. Both construction can change something in enviroment like a global variable, object position and so on...
Also, both constrinction can receive some input data. For exmaple, Sub fn(value1 As Integer) recieves one value integer datatype. The variable defines automatically inside the subroutine and avaliable inside Sub only. This variable will be auto deleted after the Sub is ended.
Lets create a function for convertion number to string by "temperature rule". Because we need returning value we have to use Function.
Function ConvertToTextTemp(input As Double) As String
If input > 0 Then
ConvertToTextTemp = "+" & CStr(input)
Else
ConvertToTextTemp = CStr(input)
End If
End Function
Dim str As String = ConvertToTextTemp(17)
println(str)
println(ConvertToTextTemp(-3))
Note:
- the line of function defining has the data type of returning value
- to return the value, just assign the output value to the function name
- I used system subroutine
printlnfor printing text string into the console. This subroutine is very useful for finding errors in code (debug). You can copy and paste this code and try to rut it. Don't forget to look into the console ;)
Subroutine (that haven't return value) is defined and used as a function. Only you don't need to define the return data type and don't return.
Sub PrintTemp(input As Double)
If input > 0 Then
println("+" & CStr(input))
Else
println(CStr(input))
End If
End Sub
PrintTemp(17)
PrintTemp(-3)
The differences between "Sub" and "Function":
- instead "Function" is written "Sub"
- "Sub" returns nothing — so, returned type specified only in "Function"
- if I want to affect to containers or the scene I write it inside a "Sub". If I want to calculate something and use returned value inside the script I use "Function"
6. Object
The object is the way to controlling data and functions more like in real life. We intuitively define each object in the life some properties and abilities to do something. For example, some dog has 5-year-old, pink colour, etc... Thus, programming "objects" just reflects reality. It's like a list or array, but with different data types and functions. For example, object "Container" contains properties "Name", "Active"(visibility), "Count of sub-containers", etc... "Container" also has functions "Create new sub-container", "Get first sub-object", etc... All possible variables and functions are in the documentation! Please feel free to look there! ;)
Access to all properties and functions of an object gets by dot character "." — for example container.name. You can call sub-object and sub-properties consistently through points this.alpha.value
Some properties can have the status "read only". It can be read but not changed. All other properties you can read and rewrite. For example, we can get the name of container println(this.name) or rename it this.name = "new_name". But we can't change directly "Count sub-containers" property. The property will be changed if we change the real count of sub-containers.
- by the way, the variable "this" refers to the current container where script placed
Some functions of the object return another object. For example, let's get an "Omo" plugin on the current container and change counter of visible sub-object:
Dim pi_omo As PluginInstance
pi_omo = this.GetFunctionPluginInstance("Omo")
pi_omo.SetParameterInteger("vis_con", 3)
Note:
- pi_omo variable is unusual datatype like Double or String. PluginInstance objects that represent a plugin. You can find all possible objects in the documentation. There is written certain datatype of function return.
- because PluginInstance is the universal datatype of any plugins, it hasn't directly access to "vis_con" properties. Unfortunately, it's not possible to write
pi_omo.vis_con = 3SetParameterInteger("vis_con", 3). The order of the input values is in the documentation.
There is not possible to create your own new type object. :( We can say that all object reflects some existing entity of VizEngine or scene. But you can create your own structures! The structure is the same as an object... but it has only properties, without functions. Details and examples later (or take a look in the documentation). The need for structures is really rare in scripts.
7. Callback function (Event)
This isn't a basic thing. But using of events we met very often into the vizrt scripts and you should know them from the beginning.
The callback function is a function that is called automatically by an external event. VizEngine tries to find in your script the appropriate function in the event moment. If VizEngine finds it then calling it. Therefore, the format of callback functions is so strong. You can't change the name of function and order input data. But there is a little convenient. Full list of all possible callback function is right at hand. Thus, you don't need you to remember them.
List of avaliable callbacks
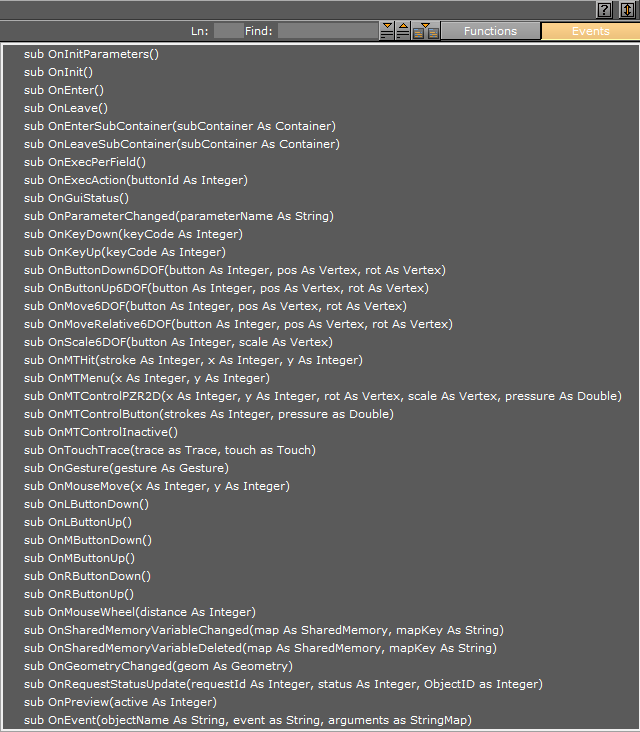
Of course, you can call callback functions by hand if it needs. For example, there is OnInit() function where must be placed start assigns. This code will be launched automatically just after starting the script and after scene loading. If I need to set variables to defaults I can call OnInit() where I want in my code. I do that usually when I want to refresh links to container and properties from the script interface. Any changing of interface calls callback function OnParameterChanged(). I just put OnInit() into the OnParameterChanged():
Sub OnInit()
scale = GetParameterDouble("scale")
target = GetParameterContainer("target")
End Sub
sub OnParameterChanged(parameterName As String)
OnInit()
End Sub
So, the initializing happens very rare and only when it needs. ;)
The most popular callback function (event) in the event of render frame tick — OnExecPerField. The function automatically is calling in each frame. Warning! Do, not accurate timer based on the OnExecPerField function. Even in the best performance computer, FPS isn't equal to 50 always. But for most common applications is enough. :)
Example of using OnExecPerField: there is 360 degrees rotation for some count frames (50 is about second).
Dim angle As Double = 0
Dim step As Double = 360.0/50.0
Sub OnExecPerField()
angle += step
if angle >= 360 then angle = 0
this.rotation.z = angle
End Sub
Note:
- I used short form of increment
angle += step. Of course, I could writeangle = angle + step. But the short form is more understandable and shorter ;) I've told to the program "Please increase angle by step" —angle += step. - I added float dots into dividing
360.0/50.0. I did this especially to avoiding integer division errors. I clarify to the compiler that it's must not simplify here and, please, divide them as rational numbers (as float, not integer). - I didn't check strict equality
if angle == 360! I have to check it with some margin in case of calculation accuracy errorif angle >= 360. This way I guarantee reliability the script. And, it's the "best practice".
If add this script to any container, it will start to rotate counterclockwise one turn by one-second approximately. If your render has 60 fps, it will rotation little faster.
One more example with OnExecPerField(). Try to understand what it does?
Dim step As Double = 2.0
Sub OnExecPerField()
this.alpha.value -= step
if this.alpha.value <= 0 then this.alpha.value = 100.0
End Sub
Show answer
It's just a simple effect of blinking. Object reveals in a flash and smoothly hides in 50 frames (by alpha).Homework
- Rewrite the script of rotations for the ability to drop it to dozen object and it wouldn't have a similar angle of rotation. Hint: random number gets by system function Random(360), where "360" is the maximum value, and the minimum is zero always.
- Write a script that will shake the current container by rotation. For example, 10 degrees to and fro. Make it with easy changing shaking degree as a default setting. Additional task: add extra shaking by position.
- More difficult task You will have to look in documentation;) Write a script for "infinity" shifting of looped texture on the current container. Hint: the whole loop of the texture is 10 only if the texture scale is 1.